Navigating Southeast Asia’s Food Delivery Boom: Opportunities and Challenges for Global Investors
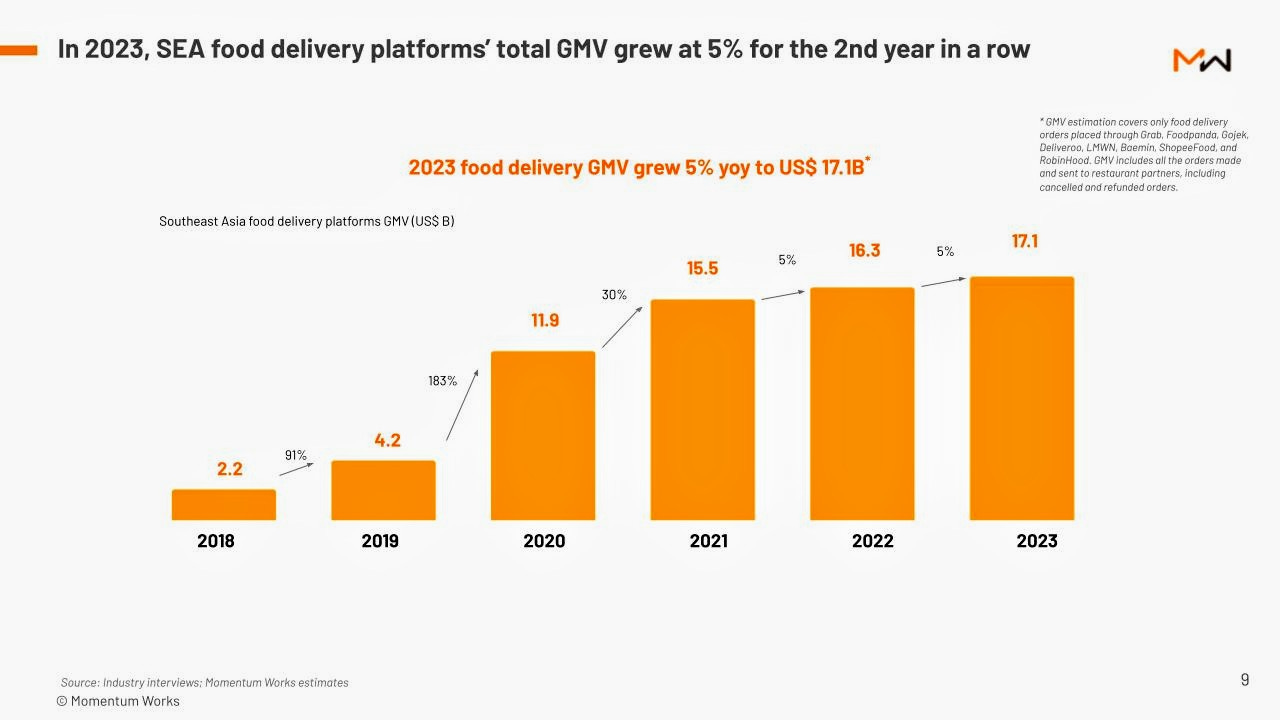
The Southeast Asian food delivery market has experienced notable developments in recent years, presenting both opportunities and challenges for global investors and the broader economy. According to Momentum Works’ “Food Delivery Platforms in Southeast Asia 2024” report, the region’s Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) for food delivery platforms reached US$17.1 billion in 2023, marking a modest 5% year-on-year growth, consistent with the previous year’s performance.
Market Dynamics and Key Players
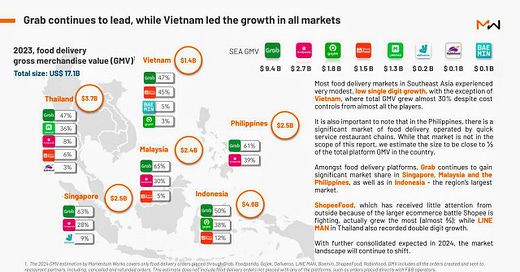
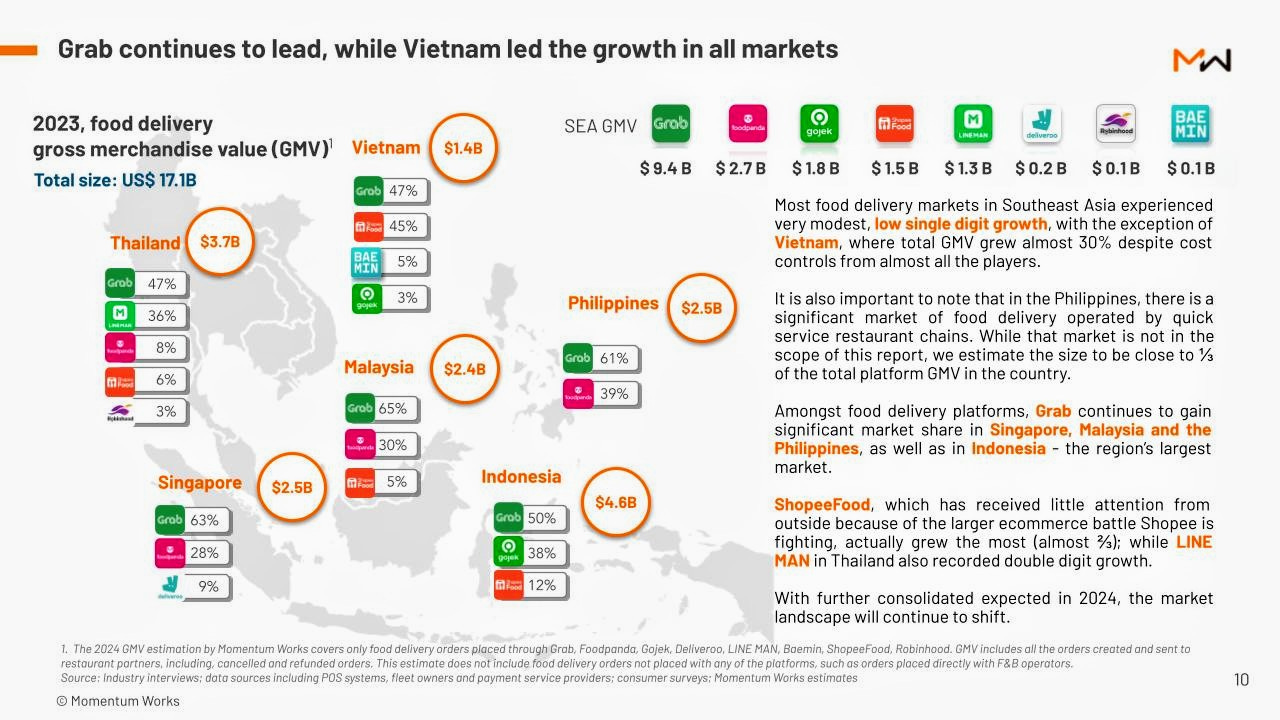
Grab continues to dominate the Southeast Asian food delivery landscape, commanding 55% of the market share, which translates to approximately US$9.4 billion in GMV — a 6.8% increase from the prior year. In contrast, competitors like Foodpanda and Gojek have seen declines, holding 15.8% and 10.5% of the market share, respectively. Notably, ShopeeFood and LINEMAN have demonstrated significant growth, contributing 8.8% and 8.1% to the region’s GMV, respectively.
Vietnam emerged as a standout market, experiencing a remarkable 27% growth in GMV, adding US$0.3 billion. Malaysia followed with a 9% increase, contributing an additional US$0.2 billion. Conversely, markets like Thailand and Indonesia reported low single-digit growth, while Singapore’s figures remained flat.
Strategic Shifts Towards Profitability
In response to ongoing pressures to achieve sustainable profitability, major food delivery platforms have reduced subsidies and adopted differentiated strategies. This shift indicates a maturation of the market, moving away from aggressive customer acquisition tactics towards a focus on financial sustainability.
Financial Projections and Investment Implications
For global investors, the food delivery sector in Southeast Asia presents significant growth potential, particularly for dominant players like Grab and GoTo Gojek. Financial forecasts suggest a promising outlook:
Grab is expected to grow earnings by 43.4% per year and revenue by 14.7% per year over the next three to five years. Additionally, its Earnings Per Share (EPS) is forecast to grow by 44% per year.
GoTo Gojek is projected to experience even more rapid expansion, with earnings growth of 130.5% per year and revenue growth of 13% per year. The company’s EPS is expected to grow by 128.4% per year.
These figures indicate that despite current market challenges, leading platforms are on track for substantial financial improvement. However, competition remains intense, with consolidation trends such as the advanced merger discussions between Grab and GoTo reflecting the need for scale to drive profitability.
Combined, the companies are worth nearly US$25 billion. GoTo, however, said in a filing on February 4, 2025 that it was not engaged in discussions about a potential merger transaction with any party, noting media reports involving Grab Holdings. Separately, it also said “the company does not have any material corporate action plans for the next 12 months other than the implementation of share buybacks.”
The Impact of Trump’s Proposed Reciprocal Tariffs
U.S. President Trump’s proposed reciprocal tariffs, which aim to match import duties with those imposed on U.S. goods, could have indirect effects on Southeast Asia’s food delivery market. While the sector itself is predominantly domestic and not directly reliant on international trade, tariffs on key trading partners like Vietnam could create ripple effects. Potential economic slowdowns, shifts in consumer spending power, and disruptions in supply chains for imported food products may indirectly impact the food delivery industry.
Moreover, if Southeast Asian countries retaliate with countermeasures, this could influence overall economic conditions, potentially affecting investor sentiment and the operational costs of food delivery platforms. While the immediate effects on the industry might be minimal, long-term structural changes in trade policies could reshape the broader economic landscape in which these companies operate.
Economic Impact
The growth of food delivery platforms has significant implications for Southeast Asia’s economy. It has catalyzed the digitalization of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), particularly in the food and beverage sector, enabling them to reach a broader customer base. This digital shift contributes to economic inclusivity and offers resilience against market disruptions.
Moreover, the sector has generated employment opportunities, from delivery personnel to roles in technology and customer service. As platforms strive for profitability, there may be shifts in employment patterns, necessitating workforce adaptability and potential policy interventions to ensure fair labor practices.
Conclusion
The Southeast Asian food delivery market presents a dynamic environment with growth potential tempered by competitive and profitability challenges. For global investors, the sector offers opportunities aligned with the region's digital and economic trajectory. A strategic, informed approach is essential to navigate the evolving landscape and capitalize on emerging opportunities.